通常我们会用 git init 命令来将我们所在的目录转换为一个 Git 本地仓库或者初始化一个新的空仓库。
用法
- 将当前目录转换为一个本地仓库
git init这个命令执行后会在本地生成一个 .git 的文件夹,用来追踪仓库的所有变更。效果如下:
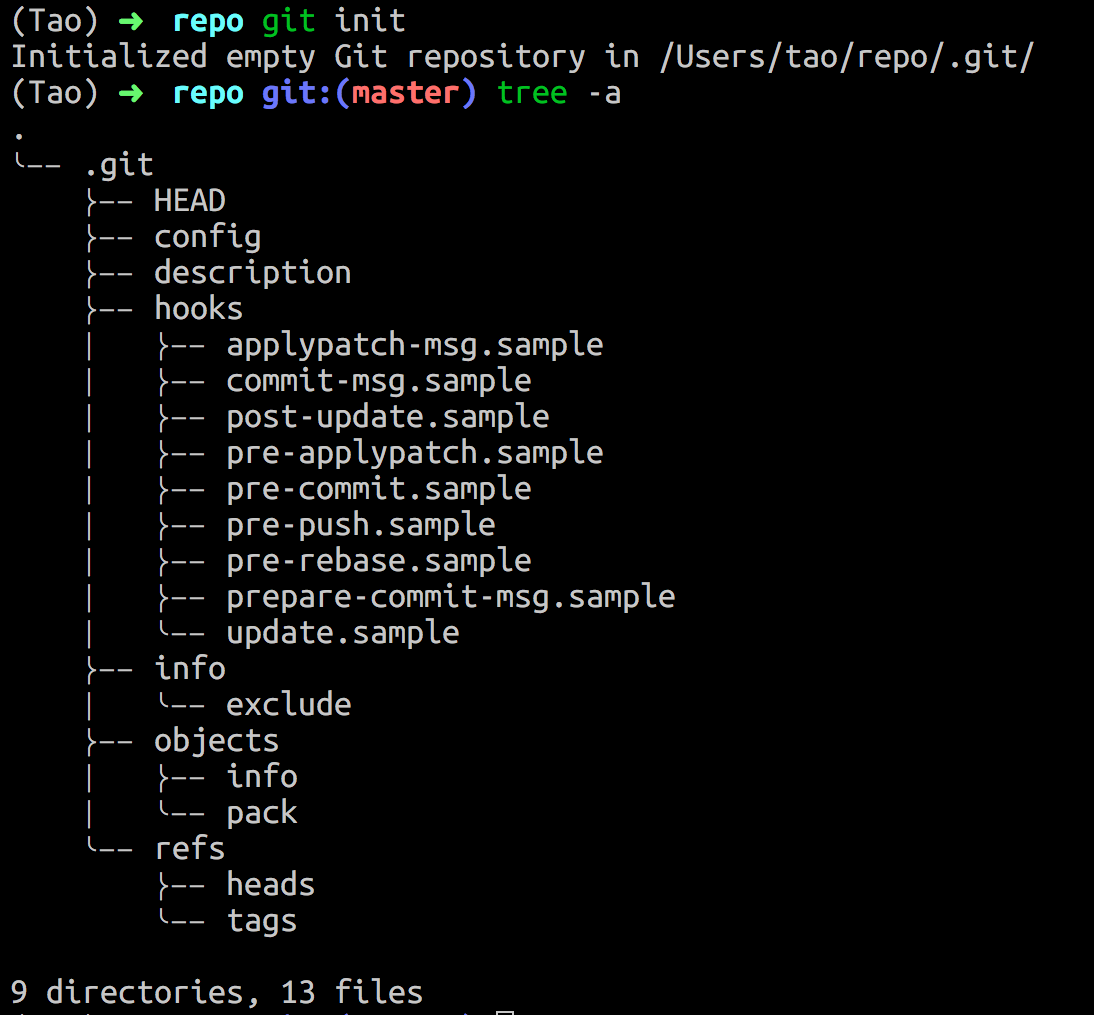
- 指定某个目录成为本地仓库
git init <repo>这个命令执行后, 将创建一个名为repo且只包含 .git 子文件夹的空目录。效果如下:
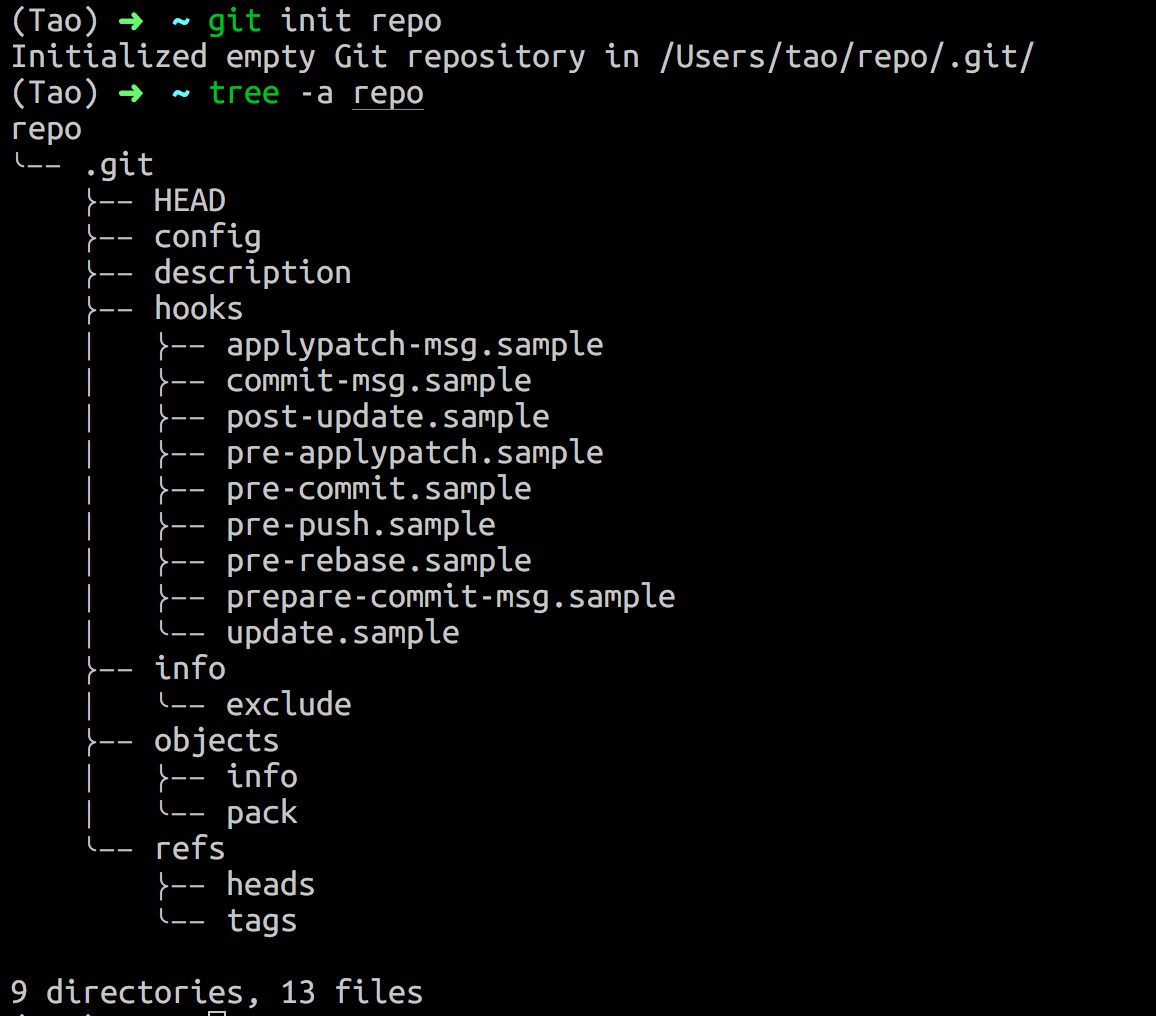
- 指定某个目录成为中心仓库(裸仓库)
git init --bare <repo> 这个命令执行后,将在本地创建一个名为 repo 的文件夹, 里面包含着 Git 的基本目录, 我们一般会将这个文件夹命名为后面加 .git 的形式,如 repo.git (这也是为什么我们从 GitHub clone 仓库的时候,地址都是 xxx.git 这样的形式的原因)。效果如下:
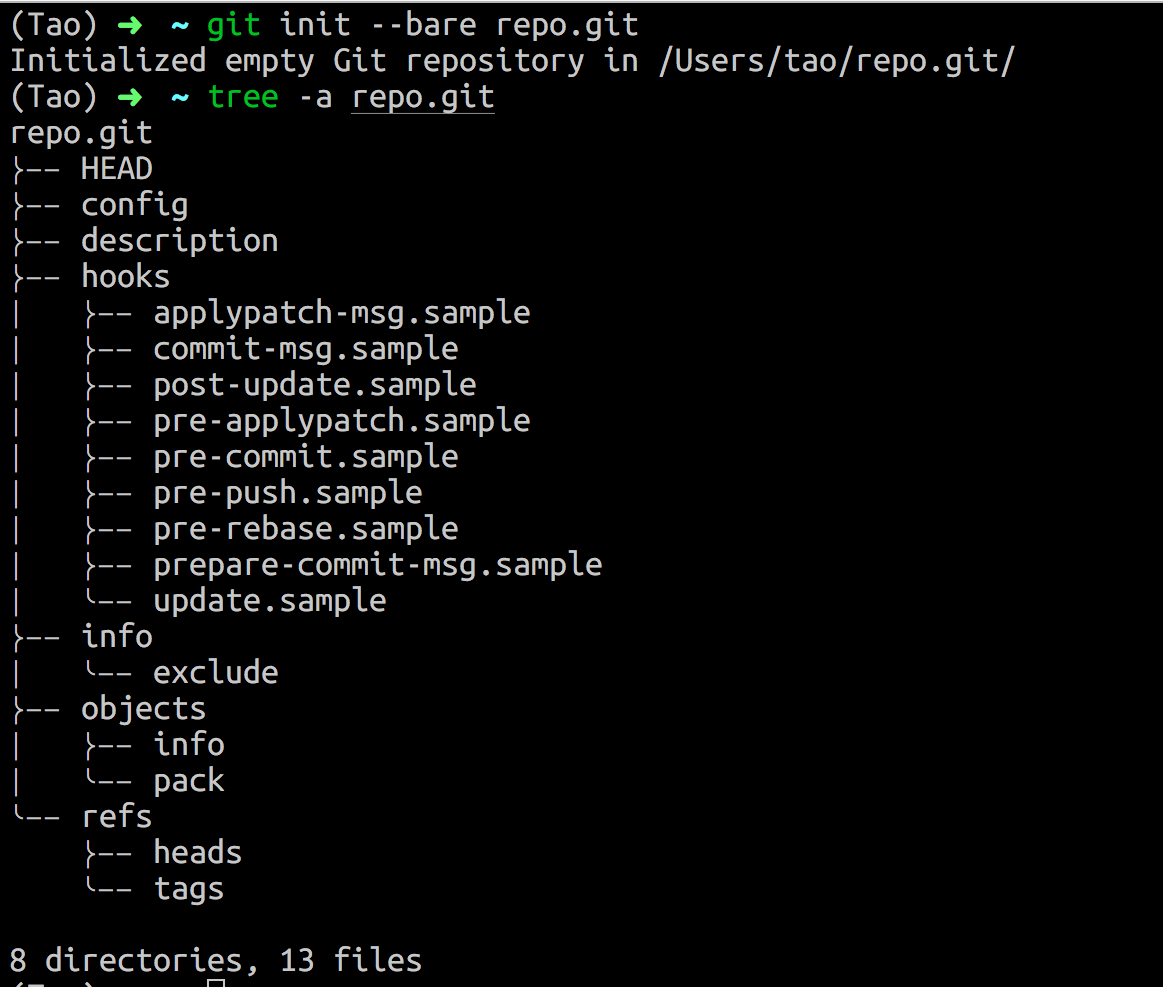
详细说一下使用 --bare 参数的含义,使用 --bare 参数初始化的仓库,我们一般称之为裸仓库, 因为这样创建的仓库并不包含 工作区 , 也就是说,我们并不能在这个目录下执行我们一般使用的 Git 命令。
对比
我们来对比一下直接使用 git init 创建的仓库和加了 --bare 参数的两个仓库。 我们直接看两个仓库的的 config 文件中的内容:
- 直接
git init创建的仓库:
[core]
repositoryformatversion = 0
filemode = true
bare = false
logallrefupdates = true
ignorecase = true
precomposeunicode = true
- 加了
--bare创建的裸仓库:
[core]
repositoryformatversion = 0
filemode = true
bare = true
ignorecase = true
precomposeunicode = true
可以看到最直观的差异在于 bare 配置项是否为 true , 此外不加 --bare 创建的本地仓库配置中有一项 logallrefupdates = true , 作用根据名字就可以看出来, 记录所有的 ref (引用) 更新, 关于 ref 的部分之后有时间可以再写,这个配置可以理解为是 Git 的一道防线。
功能差异
我们可以使用最简单的例子演示一下。
# 直接创建本地仓库
(Tao) ➜ git init repo
# 创建裸仓库
(Tao) ➜ git init --bare repo.git
# 分别 clone 两个仓库
(Tao) ➜ git clone repo c1
Cloning into 'c1'...
warning: You appear to have cloned an empty repository.
done.
(Tao) ➜ git clone repo.git c2
Cloning into 'c2'...
warning: You appear to have cloned an empty repository.
done.
# 进入 c1 仓库
(Tao) ➜ cd c1
(Tao) ➜ c1 git:(master) touch test
(Tao) ➜ c1 git:(master) ✗ g add -A
(Tao) ➜ c1 git:(master) ✗ g commit -m "test commit"
[master (root-commit) b1e32ad] test commit
1 file changed, 0 insertions(+), 0 deletions(-)
create mode 100644 test
(Tao) ➜ c1 git:(master) git push origin master
Counting objects: 3, done.
Writing objects: 100% (3/3), 200 bytes | 0 bytes/s, done.
Total 3 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0)
remote: error: refusing to update checked out branch: refs/heads/master
remote: error: By default, updating the current branch in a non-bare repository
remote: error: is denied, because it will make the index and work tree inconsistent
remote: error: with what you pushed, and will require 'git reset --hard' to match
remote: error: the work tree to HEAD.
remote: error:
remote: error: You can set 'receive.denyCurrentBranch' configuration variable to
remote: error: 'ignore' or 'warn' in the remote repository to allow pushing into
remote: error: its current branch; however, this is not recommended unless you
remote: error: arranged to update its work tree to match what you pushed in some
remote: error: other way.
remote: error:
remote: error: To squelch this message and still keep the default behaviour, set
remote: error: 'receive.denyCurrentBranch' configuration variable to 'refuse'.
To /Users/tao/repo
! [remote rejected] master -> master (branch is currently checked out)
error: failed to push some refs to '/Users/tao/repo'
# 进入 c2 仓库重复执行
(Tao) ➜ c1 git:(master) cd ../c2
(Tao) ➜ c2 git:(master) touch test
(Tao) ➜ c2 git:(master) ✗ git add -A
(Tao) ➜ c2 git:(master) ✗ git commit -m "test commit"
[master (root-commit) 7aacc58] test commit
1 file changed, 0 insertions(+), 0 deletions(-)
create mode 100644 test
(Tao) ➜ c2 git:(master) git push origin master
Counting objects: 3, done.
Writing objects: 100% (3/3), 201 bytes | 0 bytes/s, done.
Total 3 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0)
To /Users/tao/repo.git
* [new branch] master -> master
从裸仓库 clone 下来的本地仓库可以进行正常的 push 操作, 但是从一般仓库 clone 下来的本地仓库却不行。 这也正是裸仓库存在的意义。 裸仓库一般情况下是作为远端的中心仓库而存在的。
总结
使用 git init --bare <repo> 可以创建一个裸仓库,并且这个仓库是可以被正常 clone 和 push 更新的, 裸仓库不包含工作区,所以并不会存在在裸仓库上直接提交变更的情况。
Comments